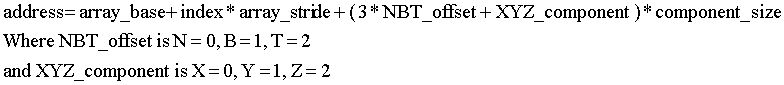
#include <revolution/gx.h> void GXNormal3f32( f32 x, f32 y, f32 z ); void GXNormal3s16( s16 x, s16 y, s16 z ); void GXNormal3s8 ( s8 x, s8 y, s8 z ); void GXNormal1x16( u16 index ); void GXNormal1x8 ( u8 index );
Depends on the function being called.
None.
These functions are used to specify normal data for a vertex. They can be called only between the GXBegin and GXEnd functions. Function names take the following format:
GXNormal[n][t]
The function name parameter n is one of {1, 3} and indicates the number of arguments to the function. The function name parameter t is one of {s8, s16, f32, x8, x16} and describes the type of each argument to the function. The type name indicates signed (s), floating point (f), and index (x) data types. The subsequent number indicates the data size in bits, so s8 indicates a signed 8-bit quantity. Consequently, the GXNormal3f32 function takes 3 floating-point arguments.
The selected function must correspond to the current vertex descriptor and the vertex attribute format specified in GXBegin. The current vertex descriptor is set using the GXSetVtxDesc function. The vertex attribute format is set using the GXSetVtxAttrFmt function.
Normals come in two flavors, GX_VA_NRM and GX_VA_NBT. The attribute GX_VA_NRM is a 3-element normal (that is, one normalized vector). The attribute GX_VA_NBT actually specifies 3 normalized vectors: normal, binormal, and tangent. Each of these has three elements. These three vectors are usually orthogonal and used for bump mapping and other special rendering techniques. To specify directly referenced data for a GX_VA_NBT attribute, simply call the appropriate GXNormal[n][t] function three times.
GXBegin(GX_TRIANGLES, GX_VTXFMT0, n);
GXPosition3f32 ( px, py, pz );
GXNormal3f32 ( nx, ny, nz );
GXNormal3f32 ( bx, by, bz );
GXNormal3f32 ( tx, ty, tz );
// ...
GXEnd();
GX_VA_NBT can specify divided index reference data for each normal vector. Furthermore, for each of the three normal vectors that comprise the NBT there are tacit offsets. For divided indices, the attribute address is computed as follows:
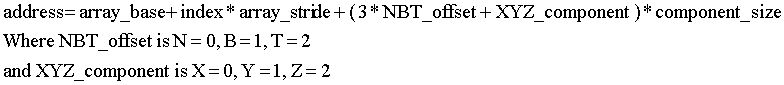
For the application, GXSetVtxAttrFmt specifies the number of components in GX_NRM_NBT3, which specifies the divided NBT indices. For the vertex descriptor that specifies a normal vector index reference, a single index is replaced with a specification for three divided indices.
There are two ways to set the normal vector table for NBT normal vectors. One method sets the table as an arrangement of the three normal vectors in interleave fashion. The internalized NBT offsets are used to select the correct values from this interleaved table, making this method very clean. The other method (and regardless of names, normal vectors are normal vectors) sets a single table. To implement this method, the NBT offset must be considered, adjusting the indices to counterbalance the NBT offset. In other words, it would be as follows.

Vertex functions must be called in the order specified by the GXSetVtxDesc function. Each vertex must send attributes (position coordinates, colors, normals, and so forth) in the specified order to guarantee proper parsing by the graphics hardware.
When an attribute is indexed (meaning its type, set by the GXSetVtxDesc function, is GX_INDEX8 or GX_INDEX16), the vertex function specifies an index to the data, not the data itself. The location of the array that will be indexed is described using the GXSetArray function. If an attribute is direct (meaning its type, set by the GXSetVtxDesc function, is GX_DIRECT), the vertex function sends the data. No vertex function should be called for an attribute that is disabled (that is, its type, set by the GXSetVtxDesc function, is GX_NONE). However, every vertex must at least enable GX_VA_POS.
The GXNormal[n][t] functions are implemented as inline functions in the non-debug version of the GX library for optimal performance. The GXNormal[n][t] functions are implemented as actual functions in the debug version of the GX library so the library can verify the correct order of vertex function calls between GXBegin and GXEnd (a common source of errors).
GXBegin, GXEnd, GXSetVtxDesc, GXSetVtxAttrFmt
2006/03/01 Initial version.
CONFIDENTIAL