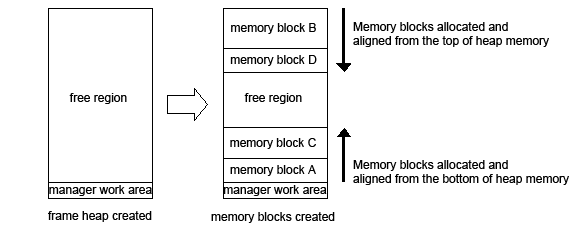
Figure 3-1 Allocating Memory for the Frame Heap
The Frame Heap Manager is a simple memory manager that can only allocate memory blocks of a specified size while all allocated memory blocks are freed simultaneously. Furthermore, the memory efficiency is good because the management information is not contained in the memory block. The following is an overview of the Frame Heap Manager.
To use the Frame Heap Manager you must create a frame heap. These functions create and destroy frame heaps.
| Functions | Functions |
MEMCreateFrmHeap | Creates the frame heap. |
MEMCreateFrmHeapEx | Creates the frame heap. Heap options can be specified. |
MEMDestroyFrmHeap | Destroys the frame heap. |
The Frame Heap Manager allocates memory blocks by filling the heap from the top and bottom without any gaps. Because this method is used to allocate memory blocks, there is no heap fragmentation. Furthermore, because there is no management region for the memory blocks that the Frame Heap Manager allocates, memory is efficiently used and processing for memory block allocation is reduced.

The following functions alblocate memory blocks.
| Functions | Functions |
MEMAllocFromFrmHeap | Allocates a memory block from frame heap. |
MEMAllocFromFrmHeapEx | Allocates a memory block from frame heap. The alignment can be specified (described in the next section). |
To allocate memory blocks from the top of the heap region, pass a negative value to the alignment argument in the MEMAllocFromFrmHeapEx function.
Even though the Frame Heap Manager does not have a memory block management region, allocated memory blocks must be aligned at 4-byte boundaries at a minimum. Allocating a 1-byte memory block consumes 4 bytes of memory.
The Frame Heap Manager can specify alignment during memory block allocation. In the MEMAllocFromFrmHeapEx function, you can specify 4, 8, 16, or 32 as alignment values. If negative values (i.e., -4, -8, -16 or -32) are specified, memory blocks are allocated from the top of the heap. The MEMAllocFromFrmHeap function does not specify alignment; the alignment value is always a value of 4.
Because the Frame Heap Manager does not manage individual allocated memory blocks, it cannot free allocated blocks individually. The Frame Heap Manager uses one of the three following methods to free memory blocks.
| Method | Content |
| Free from the bottom. | Frees memory block groups allocated from the bottom of the heap region. |
| Free from the top. | Frees memory block groups allocated from the top of the heap region. |
| Free all. | Simultaneously frees all allocated memory blocks from the heap. |
The following function frees memory blocks.
| Functions | Functions |
MEMFreeToFrmHeap | Simultaneously frees memory blocks using the specified method. |
The following methods can be specified in the MEMFreeToFrmHeap function.
| Method | Value Specified in the Function |
| Free from the bottom. | MEM_FRMHEAP_FREE_HEAD |
| Free from the top. | MEM_FRMHEAP_FREE_TAIL |
| Free all. | MEM_FRMHEAP_FREE_ALL (this code value has the same effect as simultaneously setting MEM_FRMHEAP_FREE_HEAD and MEM_FRMHEAP_FREE_TAIL.) |
The Frame Heap Manager can also save the memory block allocation status, simultaneously free the memory blocks that are subsequently allocated, and return to the status prior to saving. These features are described in the following section.
The Frame Heap Manager allows you to save the memory block allocation status for the heap region and to restore this status later. 20 bytes of memory are necessary for saving each memory block allocation status. The the memory block allocation status can be saved as many times as the heap capacity limit allows. When saving the memory block allocation status, a 4-byte tag can be attached. When restoring the memory block allocation status, the previous status or a status specified by a tag can be restored.
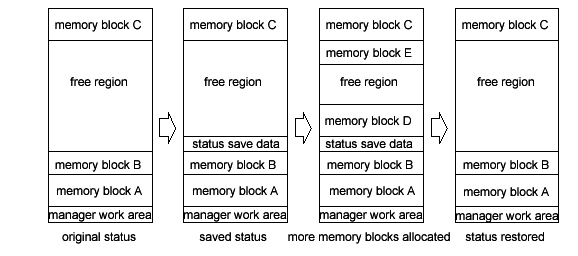
The following functions save and restore memory block allocation status.
| Functions | Functions |
MEMRecordStateForFrmHeap | Saves the memory block allocation status. |
MEMFreeByStateToFrmHeap | Restores the memory block allocation status. |
The Frame Heap Manager can reduce the heap region size to match the heap region content. Only use this functionality if memory blocks haven't been allocated from the top of the heap region. This functionality can be used to load an indefinite amount of data into memory without leaving gaps in the heap. First, create a heap that has a sufficient size, allocate memory blocks from the bottom of the heap region, and store the data. After all of the required data is stored, reduce the heap region size to match the heap content.
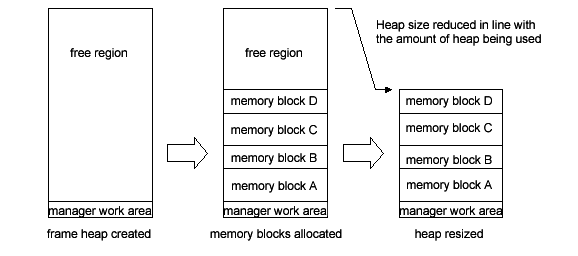
| Functions | Functions |
MEMAdjustFrmHeap | Reduces the size of the heap region by freeing unused regions at the top of the heap region. |
The memory block size can be changed with the Frame Heap Manager if the memory block is the last block allocated from the bottom of the free region in the heap. If the memory block becomes smaller than the current size, the remaining region is merged with the free region above the memory block after reduction. If the memory block becomes larger than the current size, the memory block expands into the free region above the memory block.
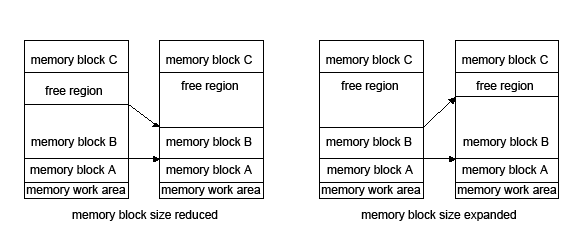
| Functions | Functions |
MEMResizeForMBlockFrmHeap | Expands or reduces memory blocks. Returns the changed memory block size. |
If the free region size is smaller than the specified size when expanding a memory block, the MEMResizeForMBlockFrmHeap function fails and returns zero.
The Frame Heap Manager can find the size of the largest allocatable memory block. These functions are shown in the following table.
| Functions | Functions |
MEMGetAllocatableSizeForFrmHeap | Gets the maximum size of the allocatable memory block. Alignment is fixed to four. |
MEMGetAllocatableSizeForFrmHeapEx | Gets the maximum size of the allocatable memory block. Alignment can be specified. |
03/01/2006 Initial version.
06/27/2006 Corrected an omission.
CONFIDENTIAL