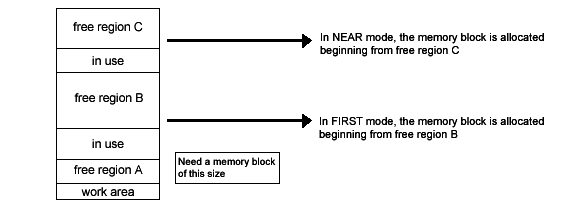
Figure 2-1 Procedure for Allocating Expanded Heap Memory Blocks
The Expanded Heap Manager and the C standard library malloc() and free() functions allocate and free memory in a similar way. In addition to allocating and freeing memory, this manager has additional functions for game programs. The following is an overview of the Expanded Heap Manager.
To use the Expanded Heap Manager, you must first create an expanded heap. The following functions create and destroy expanded heaps.
| Function | Description |
MEMCreateExpHeap | Creates the expanded heap. |
MEMCreateExpHeapEx | Creates the expanded heap. Heap options can be specified. |
MEMDestroyExpHeap | Destroys the expanded heap. |
The following functions allocate and free memory blocks.
| Function | Description |
MEMAllocFromExpHeap | Allocates a memory block from the expanded heap. |
MEMAllocFromExpHeapEx | Allocates a memory block from the expanded heap. The alignment can be specified (described in the next section). |
MEMFreeToExpHeap | Frees a memory block. |
The Expanded Heap Manager needs 16 bytes to use as a memory block management region. The minimum aligment of allocated memory blocks must be on a 4-byte boundary; therefore, even if a one-byte memory block is allocated, 20 bytes of memory are consumed.
The Expanded Heap Manager has two modes that identify free regions for allocating memory blocks. You can switch between modes. These modes are described below.
| Mode | Description |
FIRST Mode | Allocates a memory block from the first free region that is at least the size of the memory block to allocate. |
NEAR Mode | Searches for a free region nearest in size to the memory block to allocate, then allocates the memory block from this free region. |

FIRST is the default mode. Unlike FIRST, NEAR allocates a free block nearest in size to the memory block to allocate.. If an exact match isn't found, this mode searches all free regions for the nearest match. Therefore, memory block allocation takes longer if free regions are fragmented. The following functions set and acquire the allocation mode.
| Function | Description |
MEMSetAllocModeForExpHeap | Sets the allocation mode. |
MEMGetAllocModeForExpHeap | Gets the current allocation mode. |
The following are the allocation mode types that different functions use.
| Mode | Value Specified by the Function |
FIRST Mode | MEM_EXPHEAP_ALLOC_MODE_FIRST |
NEAR Mode | MEM_EXPHEAP_ALLOC_MODE_NEAR |
Generally, the Expanded Heap Manager searches for free regions from the lowest to highest address in the heap region and allocates memory blocks to the free regions starting from the bottom. As an alternative, you can search for free regions from the highest to lowest address in the heap. Using this feature, you can allocate longer–term memory blocks from the bottom of the heap region, and temporary memory blocks from the top of the heap region to help minimize heap fragmentation. For example, you can use this feature to load compressed data into memory, expand the compressed data, and then delete the compressed data source. In this case, if the expansion process is performed by allocating the memory block from the bottom of the heap region as usual, the free region is divided in half.
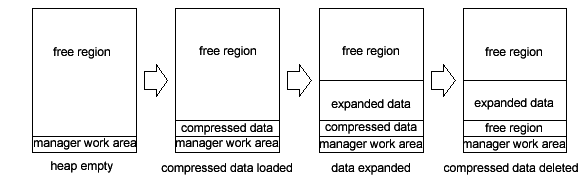
In contrast, if you temporarily load the compressed data into a memory block allocated from the top of the heap region, the free space is not divided.
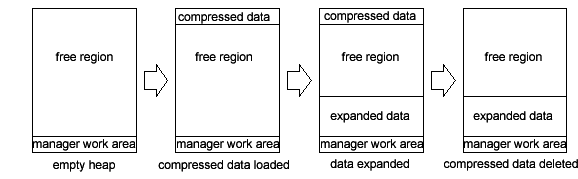
To allocate memory blocks from the top of the heap region, use the memory block allocation function MEMAllocFromExpHeapEx and pass a negative value to the alignment argument (described below).
The Expanded Heap Manager specifies alignment during memory block allocation. In the MEMAllocFromExpHeapEx function, you can specify 4, 8, 16, or 32 as alignment values. If negative values (i.e., -4, -8, -16 or -32) are specified, memory blocks are allocated from the top of the heap. The MEMAllocFromExpHeap function doesn't specify an alignment; the alignment value is always 4.
The Expanded Heap Manager can reduce the heap region size to match the heap content. Use this functionality only if memory blocks aren't allocated from the top of the heap region. Also note that the free memory that is closer to the bottom than the already allocated memory blocks don't change and reduce in size.
After placing data of undefined size and number in memory, this feature can be used to optimize the heap size when allocating additional memory is not required. First, create an extended heap with a sufficient size, allocate memory blocks from the heap region, and store the data. After storing all the required data and freeing all memory blocks allocated from the top of the heap region, reduce the heap size to match its content.
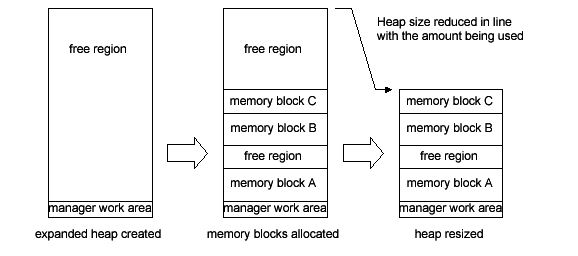
The following function reduces heap region size.
| Function | Description |
MEMAdjustExpHeap | Reduces the size of the heap region by freeing unused regions at the top of the heap region. |
If the available free space is sufficient, the Expanded Heap Manager can change the size of the allocated memory blocks without moving them. After the memory blocks are reduced to a size smaller than the original, the remaining regions are used as free regions. If the new memory blocks are larger than the original size, the memory blocks must be followed by sufficient free space. If free regions follow the memory blocks, this function merges the free regions with the memory block to increase the size of the memory block.
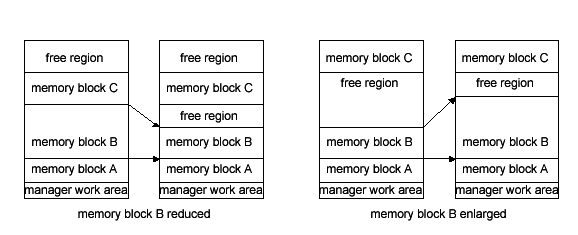
Use this function to change memory block size.
| Function | Description |
MEMResizeForMBlockExpHeap | Expands or reduces memory blocks. Returns the changed memory block size. |
If the specified size is slightly different than the size of the current memory block after reduction, in some cases a free region can't be used. In such cases, the MEMResizeForMBlockExpHeap function doesn't reduce the memory block size and returns the size of the current memory block. If you attempt to expand memory block size when there is either no free region directly after the memory block, or if it was not possible to achieve the required expansion after defragmenting the free space behind the current memory block, MEMResizeForMBlockExpHeap fails and returns zero.
The Expanded Heap Manager can obtain the total free regions. It can also obtain the size of the largest allocatable memory block. Those specific functions are shown in the following table.
| Function | Description |
MEMGetTotalFreeSizeForExpHeap | Gets the total size of the free region in the expanded heap. |
MEMGetAllocatableSizeForExpHeap | Gets the maximum size of the allocatable memory block. Alignment is fixed to four. |
MEMGetAllocatableSizeForExpHeapEx | Gets the maximum size of the allocatable memory block. Alignment can be specified. |
When the Expanded Heap Manager acquires memory blocks, group IDs from 0 through 255 are stored in the memory block management region. A froup ID can be modified as necessary. When a group ID is changed, the change occurs during the next memory block allocation. The group ID is used for the following purposes.
The following functions set and get group IDs.
| Function | Description |
MEMSetGroupIDForExpHeap | Sets the group ID of the expanded heap. |
MEMGetGroupIDForExpHeap | Gets the group ID of the expanded heap. |
The expanded heap manager can perform user specified processes on the allocated memory block. With this functionality, you can perform various processes on the heap that are unavailable in the Expanded Heap Manager. Below are some examples.
This function runs the following process.
| Function | Description |
MEMVisitAllocatedForExpHeap | Calls a user specified function for each allocated memory block. |
The Expanded Heap Manager can get allocated memory block information that indicates memory block size, group ID, and whether the allocated memory blocks were allocated from the lowest or highest address These functions get memory block information.
| Function | Description |
MEMGetSizeForMBlockExpHeap | Gets the size of the memory block. |
MEMGetGroupIDForMBlockExpHeap | Gets the group ID of the memory block. |
MEMGetAllocDirForMBlockExpHeap | Gets the allocation direction of the memory block. |
The Expanded Heap Manager can check whether the expanded heap and allocated memory blocks from the expanded heap are destroyed. The functions that check expanded heaps and memory blocks are shown below.
| Function | Description |
MEMCheckExpHeap | Checks whether the extended heap is destroyed. |
MEMCheckForMBlockExpHeap | Checks whether the memory block is destroyed. |
03/01/2006 Initial version.