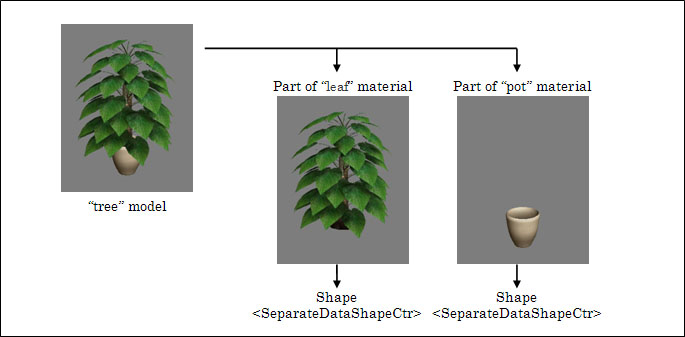
This page describes elements used to define model shape and vertex attributes data. Multiple models making up a scene can be recorded in a model data file (.cmdl). If a model consists of more than one material, primitives (polygons, etc.) for each material are grouped. The primitives grouped for each material are called shapes. A shape consists of vertex attribute data (a vertex buffer) and an index buffer that points to it. Information required to call the glDrawElement function is gathered here.

The <SeparateDataShapeCtr> element is used to define a single shape. This element basically includes a data array for vertex attributes data, an index array for defining primitives, center coordinates for the shape, skinning mode, etc.
The <Shapes> element appears inside the <SkeletalModel> element only once. It indicates the start of the definition of the <SeparateDataShapeCtr> element. If a scene includes more than one shape, multiple <SeparateDataShapeCtr> elements can be defined.
<NintendoWareIntermediateFile> |
Elements for the vertex coordinates, normal vector, and texture coordinates making up a shape are called vertex attributes. This data is called vertex attributes data. The elements listed in the table below are included in the vertex attributes that make up a shape. The required combinations of vertex attributes are determined based on the material and shading. Typically, shapes have multiple instances of vertex attributes data.
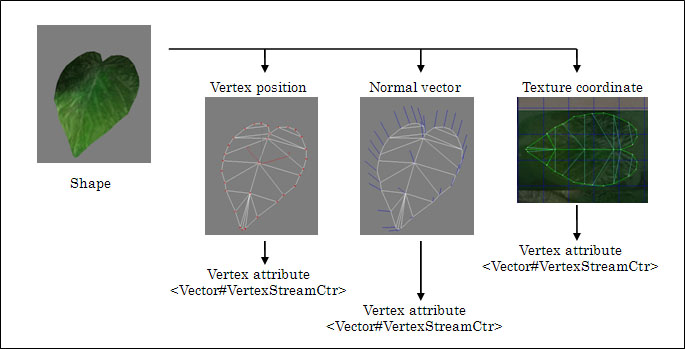
Actual data is defined for each vertex attribute. The <Vector#VertexStreamCtr> element is used to define the data for each vertex attribute. Here, # represents the number of elements and indicates the number of numeric values per vertex. It is used to stand for any one of 1, 2, 3 or 4. This element basically includes the type of attribute, number of data items, and numeric type.
If attributes with a fixed value are included among the vertices in a shape, constant data can be used instead of data strings. (For example, the normal vector for a planar model fits this description. ) This allows data size to be kept small. The <Vector#VertexAttributeCtr> element, as opposed to the <Vector#VertexStreamCtr> element, is used for the constant data.
The <VertexAttributes> element appears inside the <SeparateDataShapeCtr> element only once. It indicates the start of the definition of the <Vector#VertexStreamCtr> element. If a shape includes more than one vertex attribute, multiple <Vector#VertexStreamCtr> elements can be defined.
<NintendoWareIntermediateFile> |
The size of binary data at runtime can be reduced by using a fixed-point (integer type) format for the numeric values of vertex attribute data. The act of converting the data values to fixed-point format is called quantization and is set in the <Vector#VertexStreamCtr> element. You can apply a different quantization to each vertex attribute. Data values converted to fixed-point format can be restored to their original values by applying a floating point scaling value. For example, if the scaling value is 0.00390625 (= 1/256), 256 is restored to 1.0 and 128 is restored to 0.5. The different types of fixed-point formats are shown in the table below. Note that the fixed-point format type and scaling value used for restoration are independent parameters. The scaling value is not determinant on the range of fixed-point format types.
| Type | Description |
| Short | 16-bit signed integer. Set from -32768 (minimum) to 32767 (maximum). |
| Ushort | 16-bit unsigned integer. Set from 0 (minimum) to 65535 (maximum). |
| Byte | 8-bit signed integer. Set from -128 (minimum) to 127 (maximum). |
| Ubyte | 8-bit unsigned integer. Set from 0 (minimum) to 255 (maximum). |
In order to minimize conversion errors when vertex coordinates are expressed as floating-point numbers or fixed-point numbers, large coordinate values that represent positions far away from the origin are offset to be closer to 0.0 and then quantized.
Large value = Small value near 0.0 + Offset value.
This gives you small values and reduces error.
The use of the offset is particularly important with the fixed-point format, since the range of values is limited (see the previous section: Quantization Integer Types)
This offset value can be specified for each shape.
The <PositionOffset> element is used to define the offset value for vertex coordinates. The <PositionOffset> element only appears once in the <SeparateDataShapeCtr> element.
<NintendoWareIntermediateFile> |
Vertex coordinate values are ultimately restored in the following way:
Original value = (Scaling value x Post-conversion value) + Offset value.
Primitives available for rendering can be defined as triangles, lines or points by indexing the data strings representing vertex attribute data. The <PrimitiveSetCtr> element is used to define primitives. This element basically includes the type of primitive, index array, and skinning parameters. (Skinning parameters are required even for fixed shapes that do not undergo skinning.) For details, see the page Definition of a Scene's Hierarchical Structure.)
Primitive types include those given in the table below. The <UbyteIndexStreamCtr> element is used to define the primitive type and index array.
The <PrimitiveSets> element appears inside the <SeparateDataShapeCtr> element only once. It indicates the start of the definition of the <PrimitiveSetCtr> element. If a shape includes more than one primitive, multiple <PrimitiveSetCtr> elements can be defined. Shapes and primitives have a one-to-one correspondence for models that do not undergo skinning. However, a shape may be split up into multiple primitives for models that do undergo skinning. For details see, Defining Skinning
<NintendoWareIntermediateFile> |
The <UbyteIndexStreamCtr> element for defining index arrays appears in the <PrimitiveSetCtr> element only once. The hierarchy from the <PrimitiveSetCtr> element to the <UbyteIndexStreamCtr> element is fixed.
: |
| Type | Description |
| Points | Point primitive. |
| Lines | Line primitive. |
| LineStrip | Line strip primitive. |
| Triangles | Triangle list primitive. |
| TriangleStrip | Triangle strip primitive. |
| TriangleFan | Triangle fan primitive. |
| PointSprites | Point sprite primitive. |
| SilhouetteTriangles | Triangle list primitive with silhouette. |
| SilhouetteStrip | Triangle strip primitive with silhouette. |
| Subdivision | Subdivision primitive. |
| SubdivisionLoop | Subdivision loop primitive. |
CONFIDENTIAL