Vertex Lighting
This section describes the vertex lighting.
About Vertex Lighting
Vertex lighting is the process of calculating per-vertex lighting. An RGB color value is calculated for each vertex based on factors like the position and color of the light source and the position of the vertex, after which color values between the vertices are interpolated.
The figure below shows per-vertex shading being applied by the vertex shader. Polygon density influences the lighting.
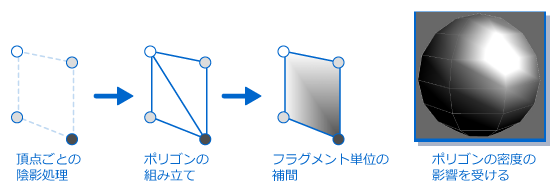
The figure depicts the process flow, from the input of data from the vertex process, through the vertex lighting done by the vertex shader based on that data, to the output of the color that results from the the lighting process.

Vertex Lighting Settings
This section describes settings for lights and materials when performing per-vertex lighting.
Light Settings
The table below lists the items which can be set for each type of light.
| Categories | Item | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Light color | Ambient color (environment light) |
The color and alpha values for the light that will effect the ambient color of the material. |
| Diffuse color (scattered light) |
The color and alpha values for the light that will effect the diffuse color of the material. | |
| Sky color | A parameter that can be set for hemispherical light. The color of the light that influences vertices with the normal pointing upward. | |
| Ground color |
A parameter that can be set for hemispherical light. The color of the light that influences vertices with the normal pointing downward. | |
| Light orientation | Position | The light position. For vertex light, this is set in the world coordinate system. |
| Direction: | The light direction. For vertex light, this is set in the world coordinate system. By combining the nodes and hierarchies of animations you can inherit values from the top level. | |
| Light attenuation factors | Distance attenuation | Specifies how far the light will reach in terms of an attenuation rate Used for point lights and spotlights. |
| Spotlight attenuation | Specifies how wide the light will reach in terms of an attenuation rate using a lookup table. Used for spotlights. | |
| Sky color weight | A parameter that can be set for hemispherical light. Setting the sky color weight closer to 1 makes the sky color stronger, and setting the weight closer to 0 makes the ground color stronger. |
Type of usable lights
The figure below depicts the kinds of lights that can be used for vertex lighting, and how light spreads from each kind of light.
The more lights you use, the greater the processing load for that fragment.

Hemispherical Lights
Hemispherical light is lighting that illuminates and reflects from the inside of a giant sphere. The model is illuminated from one hemisphere by the sky color, and from the other hemisphere by the ground color. By setting the sky color and ground color in accordance to the scene, you can achieve the effect of receiving indirect light.
The figure below depicts how light spreads from a hemispherical light.

Material Settings
The table below lists parameters that can be set for each material.
| Categories | Item | Description |
|---|---|---|
| General | Enable occlusion | A parameter that can be set for hemispherical light. You can use the vertex alpha as set by the 3DCG to change the illumination of the hemispherical light. Although this item is called occlusion, it is specifically an item for changing the illumination of the hemispherical light using the vertex alpha. It is not an item limited to general ambient occlusion. |
| Material color | Emissive color |
Not used for vertex lighting. |
| Ambient color |
Color expressing the shaded side of the object. This is set in a material. | |
| Diffuse color |
Color expressing the surface "feel" of the object. This is set in a material. | |
| Specular color 0 |
Not used for vertex lighting. | |
| Specular color 1 |
Not used for vertex lighting. | |
| Environment light of entire scene | Global ambient color | Not used for vertex lighting. |
| Light Controls | Distribution 0 | Not used for vertex lighting. |
| Distribution 1 | Not used for vertex lighting. | |
| Reflection | Not used for vertex lighting. | |
| Fresnel | Not used for vertex lighting. |
Material color
Material color refers to the polygon model color required for vertex lighting calculations. Two colors can be set.
The figure below shows the position of each material color when light is shined on a spherical model from the upper-left direction.

Vertex Lighting Formula
This section describes the formula used when performing vertex lighting.
The figure below depicts the flow of the calculation for vertex lighting.
