Calculates a correction matrix used to make the left camera image match the right camera image in 3D space.
The nn::camera::CTR::GetStereoCameraCalibrationMatrix function returns a matrix for correcting errors in the placement of the stereo camera. Using this matrix, however, will prevent a 3D view on the edges of the screen if the position offset of the system's stereo camera is near the limit, because the edges of the area where the left and right images overlap (for convenience, we will call this the "overlapping area") will be cut off (see figure below). Although the position offset in the figure below is extreme for purposes of illustration, the actual limit of positional offset is smaller than in this figure.
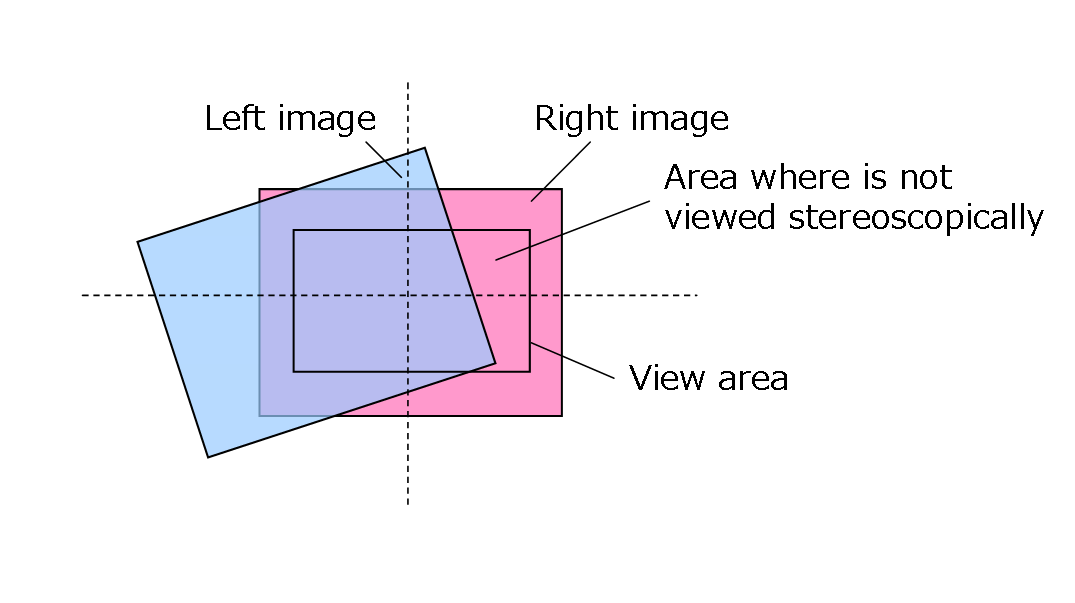
This function returns a correction matrix that will not cut off the edges of the overlapping area, even if the placement error is at the limit. It does this by enlarging the image if the overlapping area is too small.
Unless you have a specific reason, we recommend using this function instead of the nn::camera::CTR::GetStereoCameraCalibrationMatrix function.
The internal processing of this function is as follows.
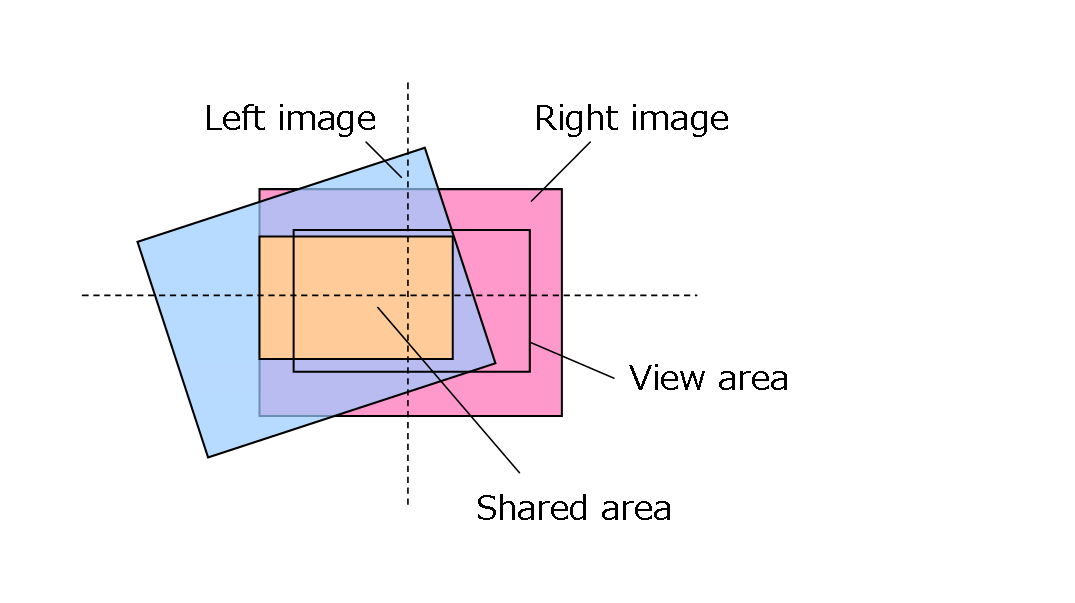
(1) Finds the rectangle where the left and right images overlap, based on the calibration data and orgWidth/orgHeight (see figure below). Here, the width : height ratio of the rectangle is dstWidth : dstHeight.
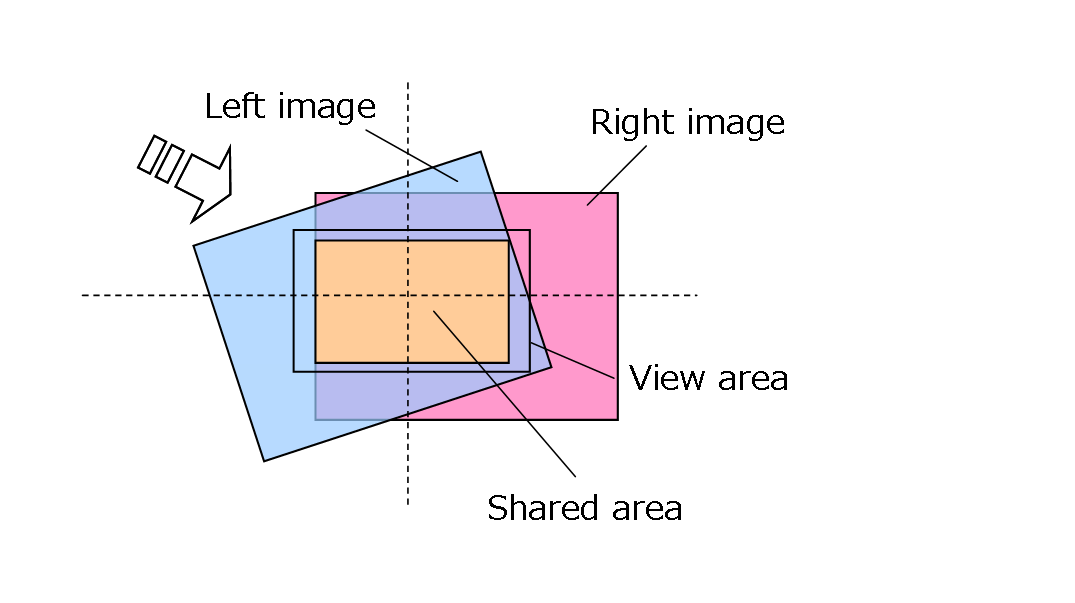
(2) If the screen is configured so that the image will appear in the center, it moves the horizontal correction matrix so that the center of the rectangle is in the center of the screen (see figure below).
(3) On some systems, the size of the rectangle may be smaller than dstWidth x dstHeight. On other systems, the size of the rectangle may be larger than dstWidth x dstHeight. Here, we scale the horizontal correction matrix so that the clipped rectangle is the same size as dstWidth x dstHeight (see figure below). For example, if the specification to the function is dstWidth = 400, dstHeight = 240, and the size of the rectangle is 320 x 192, then the correction matrix will scale to 400/320 = 1.25x.
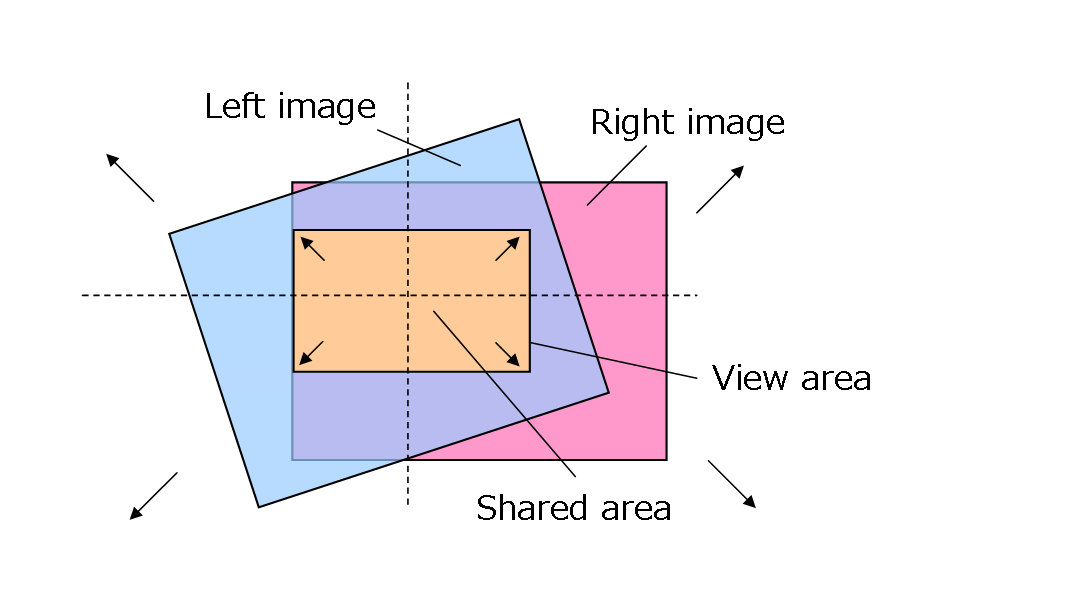
Specify in dstWidth/dstHeight the size of the overlapping rectangle to display; in other words, specify the size of image that you want the rectangle to appear as.
The correction matrix calculated by the above process is stored in pDstR and pDstL. The scale calculated in step (3), above is stored in pDstScale.
The output correction matrix is used to move the camera image horizontally. This matrix is simply a three-dimensional extension of a two-dimensional matrix that expands and shrinks images, rotates around the light axis, and performs horizontal and vertical translations; it does not include three-dimensional transformations, such as rotations about the horizontal and vertical axes.