This section presents an overview of player heap operations and how to use it.
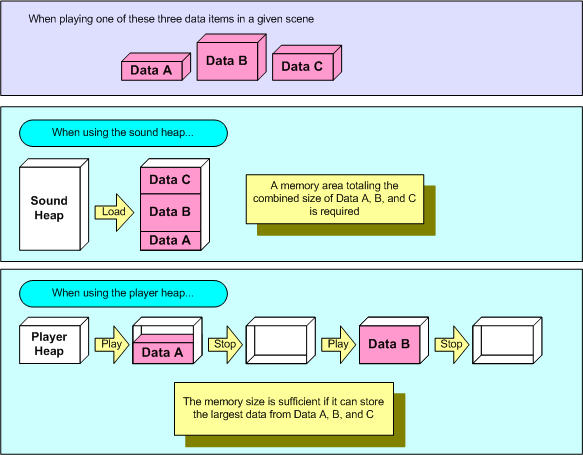
Under the NW4C sound development environment, a conventional sound heap is used as a method of managing memory used by snd library. To create a sound heap, it is first necessary to collect the sound data required by a scene into a unit called a "group." For example, assume there are dozens of tracks of BGM sequence data that can be played in a given scene. In this case, you must include all sequence data in a group which in turn requires a large amount of memory. It is possible to minimize the amount of memory consumed in cases like this by using a player heap.
In contrast to manually loading sound data when using a sound heap, with a player heap you can automatically load sounds when playback is set to start and automatically release them at the point playback ends. A released heap can be used to load the sound data to be played next.
The following example shows the difference between using a sound heap and using a player heap.

In this way, it is possible to play all sequences as long as the size of the player heap is large enough to load the sequence data having the largest data size out of all the BGM sequence data that can be played for the given scene.
Player heap settings are made for a Player. Specify the size of the player heap using the player heap item on the Player List.
If an attempt is made to play a sequence sound using a Player for which a player heap has been set, the sequence data will be automatically loaded into the player heap. Including sequence data in a group therefore eliminates the need to load data into the sound heap ahead of time.
If sequence data is already loaded into the sound heap even though a player heap has been configured, the data in the sound heap is used and data is not loaded into the player heap.
It is possible to load only sequence data into a player heap. Bank data, wave sound data and so on cannot be loaded.
The number of memory regions allocated for the player heap is given by the sound limit. For example, if the sound limit is three, memory three times the size specified for the player heap is consumed. Furthermore, the memory regions used for the player heap are allocated as static regions at time of initialization.
Data is loaded at time of playback start when using a player heap. A delay occurs in the start of sound playback because playback of the sound does not actually start until after data has been loaded.
If you want sounds to start immediately at the start of playback, you can implement a playback preparation process on the program side so that data is loaded in the player heap ahead of time.
CONFIDENTIAL