Texture Formats
This section describes the texture formats that can be used in CreativeStudio's Material panel.
Texture Format Types
This section describes the different kinds of texture formats you can use in CreativeStudio and presents the specifications for each.
List of Texture Formats
The table below lists the types of texture formats.

Texture Format Structure
This section describes the components that make up a texture format.
| Texture Format | Component |
|---|---|
| RGB | Holds color information. R = Red component G = Green component B = Blue component |
| A (Alpha) | Holds transparency information. |
| L (Luminance) | Holds grayscale brightness information. |
| ETC (Ericsson Texture Compression) | Compresses an RGB texture in 4x4-pixel blocks. |
| HILO | Holds only the R and G components. You can maintain a system of 256 gradations for each color component by treating the R component as the normal in the X direction and the G component as the normal in the Y direction. |
Texture Size
CreativeStudio can associate color and transparency expressions and information for controlling normal vectors with texels when attaching a texture image to a polygon.
Texel is the term for the fundamental unit representing a single point and, in contrast to pixel , refers to the non-color composition of the texture image.
In CreativeStudio, the texel operation relates texture coordinates to texels. Texel is short for "texture pixel."
The height and width of the texture image being used do not need to be the same size. Rectangular textures are also supported.
However, the height and width must both be a power of two.
A power of two is any of the integer powers of the number two (in other words, two multiplied by itself a certain number of times). There are eight powers of two between the minimum and maximum texture sizes (8 and 1024): 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, and 1024.
The following figure describes the maximum and minimum size of textures.
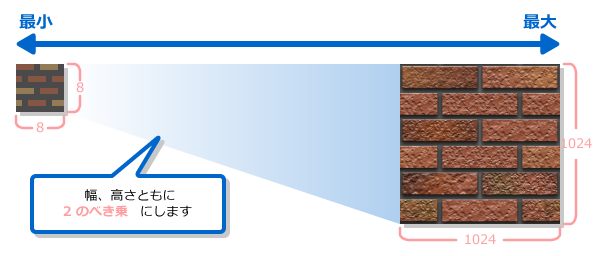
Texture formats include a minimum size that cannot be reduced any further.
- Minimum sizes by texture format
- ETC format: 16 × 16
- Other than ETC format: 8 × 8
Texture Format Properties
This section describes the properties of each texture format.
Alpha Format
This format stores only the alpha component.
Although the image is usually used as transparent, it can also be expressed as a grayscale.
Properties of the Alpha Format
| Format | RGB | Alpha | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A4 |  |
-- | This format uses 4 bits per texel. The alpha component can be expressed in 4 bits (16 levels). |
| A8 |  |
-- | This format uses 8 bits per texel. The alpha component can be expressed in 8 bits (256 levels). |
Luminance Format
This format stores only the luminance component. Although usually used as a grayscale, this format can also express alpha values.
Properties of the Luminance Format
| Format | RGB | Alpha | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| L4 |  |
-- | This format uses 4 bits per texel. Brightness can be expressed in 4 bits (16 levels). |
| L8 |  |
-- | This format uses 8 bits per texel. Brightness can be expressed in 8 bits (256 levels). |
Luminance Alhpa Format
This format stores luminance and alpha components.
Properties of the Luminance Alpha Format
| Format | RGB | Alpha | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LA4 |  |
 |
This format uses 8 bits per texel. Brightness and alpha can both be expressed in 4 bits (16 levels), respectively. |
| LA8 |  |
 |
This format uses 16 bits per texel. Brightness and alpha can both be expressed in 8 bits (256 levels), respectively. |
ETC Format
The texture size can be reduced by compressing the RGB texture.
The higher the resolution and smoother the variation in color of the image before compression, the more reproducible it will be.
Properties of the ETC Format
| Format | RGB | Alpha | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ETC |  |
-- | This format uses 4 bits per texel using compression technology. RGB components are compressed and stored in 4 bits. |
ETCA Format
This format is the same as the ETC format with an added alpha component.
RGB component properties are the same as the ETC format.
Properties of the ETCA Format
| Format | RGB | Alpha | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ETCA4 |  |
 |
This format uses 8 bits per texel using compression technology. RGB components are compressed and stored in 4 bits. The alpha component can be expressed in 4 bits (16 levels). |
HILO Format
This texture format is used for normal mapping.
You can express quasi-bumps and depressions on a polygon's surface applying normal mapping to that polygon.
Properties of the HILO Format
| Format | Images (RGB) | Alpha | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| HILO |  |
-- | This format uses 16 bits per texel and is used for normal mapping. X and Y components for normal information are stored for the R and G components using 8-bit precision. |
RGB Format
This format stores only the RGB components.
Properties of the RGB Format
| Format | RGB | Alpha | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGB565 |  |
-- | This format uses 16 bits per texel. Colors can be expressed in this format using 5 bits (32 levels) for the R component, 6 bits (64 levels) for the G component, and 5 bits (32 levels) for the B component. |
| RGB8 |  |
-- | This format uses 24 bits per texel. This format can express each of the three RGB components in 8 bits (256 levels). |
RGBA Format
This format stores the RGB components and alpha component.
Properties of the RGBA Format
| Format | RGB | Alpha | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGBA4 |  |
 |
This format uses 16 bits per texel. Each RGBA component can be expressed in 4 bits (16 levels). |
| RGB5A1 |  |
 |
This format uses 16 bits per texel. The three RGB components can be expressed in 5 bits (32 levels) and the alhpa component can be expressed in 1 bit (transparent or opaque). |
| RGBA8 |  |
 |
This format uses 32 bits per texel. Each RGBA component can be expressed in 8 bits (256 levels). Although the number of colors is greatest on the one hand, the data size is also the largest. |
Selecting a Texture Format by Application
This section describes how to select a texture by application.
Texture Format
Selecting a Texture Format by Application

Texture Formats Used for Normal Vector Mapping
There are two methods of normal mapping: one method uses the two R and G components of the texture for the normal vector, while the other uses the three RGB components.
Selecting a Texture Format for Normal Mapping
